What is an Expandable Prosthesis?
typically in the limbs (arm or leg), when a tumor or disease requires the removal of bone
tissue. What makes it unique is that the prosthesis can grow or expand over time, allowing
for adjustments as a patient’s body grows or changes.
typically in the limbs (arm or leg), when a tumor or disease requires the removal of bone
tissue. What makes it unique is that the prosthesis can grow or expand over time, allowing
for adjustments as a patient’s body grows or changes.
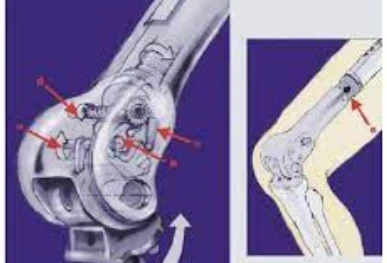
How Does Expandable Prosthesis Work?
An expandable prosthesis works by incorporating a mechanical or motorized mechanism that allows the device to expand gradually. There are typically two methods by which an expandable prosthesis can grow:
- Mechanical Expansion: In this method, the prosthesis can be lengthened manually through the use of a specialized tool. Patient will need a small surgical procedure once in every 3 -6 months to lengthen the leg.
- Motorized or Magnetic Expansion: Some advanced prostheses use a magnetic mechanism (powered by an external magnetic device) that causes the prosthesis to expand without the need for surgery. The magnets cause the components of the prosthesis to move apart, lengthening the device so no need of surgery to lengthen limb.
- Adaptability to Growth: For children and young adults whose bones are still growing, an expandable prosthesis is ideal because it adjusts as the child grows, reducing the need for multiple surgeries to replace or lengthen the prosthesis.
- Reduced Need for Surgery: Since the prosthesis can be adjusted externally, patients do not need to undergo additional surgeries to change or replace the prosthesis as they grow or as the device wears down. This minimizes the risks, recovery time, and hospital visits associated with multiple procedures.
- Improved Functionality and Comfort: Expandable prostheses are designed to closely mimic the natural range of motion and weight distribution of a healthy limb. This allows patients to regain a high level of function and comfort after surgery.
- Preservation of Limb Length: In cases of bone cancer or bone deformities, using an expandable prosthesis allows for the preservation of limb length and function, which is crucial for maintaining balance, mobility, and self-esteem.
- Long-Term Solution: Instead of needing frequent replacements, the expandable prosthesis provides a long-term solution for patients, particularly in pediatric cases.
What Are the Advantages of Expandable Prosthesis?
What Are the Disadvantages of Expandable Prosthesis?
- Risk of Complications: Like any prosthetic device, there are risks of complications, such as infection, loosening of the prosthesis, or mechanical failure. The moving parts of the prosthesis may wear down over time, which could lead to the need for repairs or adjustments.
- Cost: Expandable prostheses are more expensive than standard prostheses due to their specialized nature. Additionally, there may be ongoing costs for maintenance and adjustments.
- Limitations on Expansion: The amount of expansion possible is limited. As the patient continues to grow or change in size, the prosthesis may reach its maximum capacity, requiring replacement.
- Potential for Malfunction: If the mechanical or magnetic components that control the expansion of the prosthesis malfunction, the prosthesis may not expand correctly, leading to discomfort or the need for a revision surgery.
- Need for Regular Monitoring: While the prosthesis can be expanded externally, it still requires regular monitoring and maintenance by medical professionals to ensure that it is functioning properly and that the patient is not experiencing issues with fit or function.
- Limited in Some Areas: Expandable prostheses are more commonly used in the long bones of the arm and leg, such as the femur or tibia, and may not be appropriate for every type of bone replacement or tumor location.