What is Extended Curettage of Bone Tumor?
Extended curettage of a bone tumor is a surgical procedure used to treat benign bone tumors.
In this procedure tumor is scooped out, retaining the normal joint and bone of the patient, so
patient can near normal function post-surgery.
The term "extended" refers to the technique of aggressively removing the tumor and a wider
margin of surrounding tissue compared to traditional curettage, with the goal of reducing the
chance of recurrence.
Indicated in Tumors like – Giant Cell Tumor, Chondroblastoma, Aneurysmal Bone cyst,
Simple bone cyst, Fibrous dysplasia, Osteoblastoma
Steps of Extended Curettage of Bone Tumor
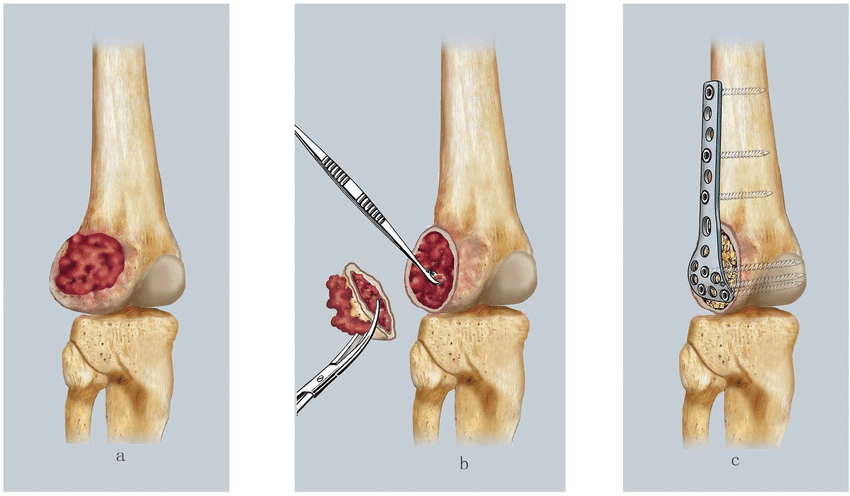
- Exposure of the Tumor: The surrounding soft tissues are carefully retracted to expose the bone and the tumor
- Curettage: The tumor is meticulously scraped out using curettage instruments. The extended approach involves removing not only the tumor itself but also a margin of healthy bone tissue around the tumor using high speed burr to ensure no residual tumor cells remain.
- Phenol application: Used to chemically treat the bone cavity and surrounding tissue to kill any remaining tumor cells.
- Cauterization: High heat may be applied to the cavity to further reduce the risk of recurrence.
- Cryotherapy: Freezing the cavity with liquid nitrogen to destroy any remaining tumor cells.
- Bone Grafting or Reconstruction: After the tumor is removed, the bone cavity may need to be filled with a bone graft (autograft or allograft) or Bone cement to maintain bone strength and function.
- Preservation of Bone Structure: Extended curettage aims to remove the tumor while preserving as much healthy bone as possible. This is important for maintaining function, especially in weight-bearing bones.
- Minimally Invasive: Compared to more extensive surgeries like bone resection or amputation, extended curettage is less invasive and requires shorter recovery times.
- Lower Recurrence Rate: The aggressive nature of extended curettage, especially with the use of adjuvant treatments like phenol, cryotherapy, or cauterization, helps reduce the risk of tumor recurrence compared to simpler curettage.
- Cosmetic and Functional Preservation: Since the procedure aims to preserve bone and joint function, it has a higher chance of maintaining limb functionality and appearance, especially if the tumor is in an area that requires movement.
- Infection: As with any surgical procedure, there is a risk of infection in the surgical site.
- Fracture/collapse of bone: The bone may become weakened during the curettage process, especially if a large portion of bone is removed. This can increase the risk of fractures or collapse post treatment.
- Tumor Recurrence: Although extended curettage reduces the risk of recurrence, there is still a possibility that the tumor may return in 10-20 percent of patients.
Adjuvant Treatment: After the tumor is removed, various adjuvant techniques may be used to reduce recurrence risk. These could include:
